Neuropathy Treatment Tulsa, OK
Our Services
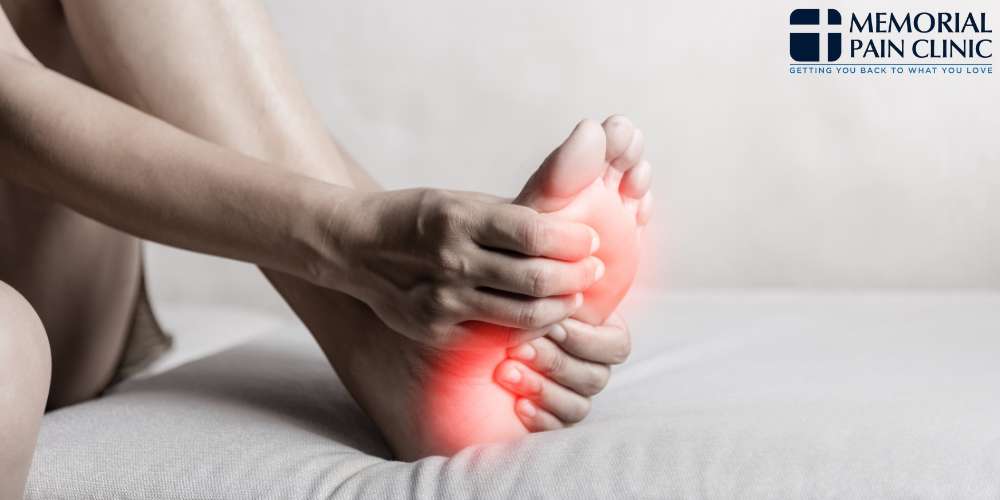
Explore comprehensive neuropathy treatment solutions at Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, OK. Our specialized pain management team is dedicated to providing effective relief for those suffering from neuropathic pain and discomfort. With a focus on personalized care and advanced treatment options, we aim to improve your quality of life by addressing the underlying causes of neuropathy and managing its symptoms effectively.
Discover how our expertise and compassionate approach can help you regain comfort and mobility. To schedule an appointment with us, please call our office at 918-200-9944 today.
What Is Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when your peripheral nervous system becomes damaged. Your peripheral nervous system is the largest nervous system in your body and includes all the nerves except your brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral neuropathy generally affects your hands and feet, causing numbness, tingling, and pain. Neuropathy may also cause you to have trouble walking or grasping things with your hands.
Traumatic injuries, infections, or heredity can all result in nerve damage. Diabetes, if left untreated, may also be a contributing cause of damage to your peripheral nerves.
Radiculopathy vs Neuropathy
Radiculopathy is a condition caused by compression, inflammation, or injury to a spinal nerve root, often resulting in severe pain, numbness, or weakness radiating along the path of the nerve. Neuropathy, on the other hand, is a broader term that refers to any disease or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which can lead to symptoms like pain, tingling, or muscle weakness, affecting various parts of the body depending on the nerves involved.
Types of Neuropathy
Neuropathic pain can manifest in various forms, each affecting different types of nerves or caused by different underlying conditions. We outline some of the most common forms of neuropathy in the following sections.
Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy affects the peripheral nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, leading to symptoms like pain, tingling, and muscle weakness, usually in the hands and feet. To avoid or prevent peripheral neuropathy, many professionals recommend avoiding alcohol and other toxins, fixing vitamin deficiencies, eating a healthy diet, exercising, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes, resulting from prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging nerves. It often affects the legs and feet, causing pain, numbness, and sometimes leading to serious foot problems.
Small Fiber Neuropathy
Small fiber neuropathy targets the small nerve fibers responsible for pain and temperature sensations. Symptoms include burning pain, tingling, and loss of pain and temperature sensations, often starting in the feet and hands.
Large Fiber Neuropathy
Large fiber neuropathy involves the large myelinated nerve fibers that control muscle movements and convey touch sensations. This can result in muscle weakness, coordination problems, and a loss of reflexes and touch sensation.
Autonomic Neuropathy
Autonomic neuropathy affects the autonomic nerves controlling involuntary body functions like heart rate, digestion, and bladder function. Symptoms include blood pressure issues, digestive problems, and abnormal sweating.
Alcoholic Neuropathy
Alcoholic neuropathy arises from excessive alcohol consumption, leading to nutritional deficiencies and direct toxic effects on nerves. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness, primarily in the extremities.
Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Ischemic optic neuropathy involves reduced blood flow to the optic nerve, leading to sudden vision loss. It can be associated with conditions like giant cell arteritis or cardiovascular disease.
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy
Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is a rare autoimmune disorder affecting motor nerves, causing asymmetric muscle weakness and atrophy, typically without sensory loss. It often starts in the hands and can progress to other areas.
Axonal Neuropathy
Axonal neuropathy refers to damage primarily to the axons, the long projections of nerve cells. It can result from various causes including toxins, metabolic disorders, and genetic conditions, leading to widespread muscle weakness and sensory disturbances.
What Are the Neuropathy Symptoms?
The painful symptoms of neuropathy vary from mild to severe and depend on which nerves are affected. Some common symptoms include:
- Numbness, prickling, or tingling in hands or feet
- Sharp, jabbing, stabbing pain
- Burning sensation in your fingers or toes
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness
- Trouble walking, lack of coordination
When your autonomic nerves are affected by neuropathy symptoms, you may experience trouble with automatic bodily functions such as bladder, bowel, or digestive issues, or have an intolerance to heat and experience uncontrollable sweating. In extreme situations, neuropathy can cause difficulty breathing, changes in blood pressure, and organ failure.
Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms
Generally, the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy affect the extremities first, then they may progress to other areas of the body. Potential symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include the following.
- Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes
- Tingling or burning sensations (paresthesia)
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, or electric-like pain
- Sensitivity to touch
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle cramping or twitching
- Difficulty walking or moving limbs
- Feeling like wearing gloves or socks when not
- Heat intolerance and altered sweating
- Digestive issues such as bloating, constipation, or diarrhea
- Changes in blood pressure, causing dizziness or lightheadedness
Diabetic Neuropathy Symptoms
As diabetic neuropathy also results from nerve damage, its symptoms are similar to peripheral neuropathy.
- Numbness or reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes, especially in the feet and hands
- Tingling or burning
- Sharp or stabbing pains
- Muscle weakness
- Loss of reflexes, especially in the ankles
- Loss of balance and coordination
- Serious foot problems, such as ulcers, infections, and bone and joint pain
- Digestive issues
- Problems with urination, such as difficulty emptying the bladder completely or incontinence
- Sexual dysfunction
- Increased or decreased sweating
- Changes in blood pressure that cause dizziness or fainting when standing up
Small Fiber Neuropathy Symptoms
The symptoms of small fiber neuropathy are similar to the symptoms for peripheral neuropathy. However, they can also include the following.
- Increased sensitivity to pain
- Itching or a crawling sensation on the skin
- Allodynia (pain from stimuli that do not usually cause pain, such as light touch)
- Dry eyes and mouth
What Causes Neuropathy?
Neuropathy can be caused by various peripheral and central nervous system issues, including diabetes, physical injury or trauma, infections like shingles or HIV, autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, genetic disorders, exposure to toxins, chronic alcoholism, nutritional deficiencies, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, and certain medications.
How Is Neuropathy Diagnosed?
To have peripheral neuropathy diagnosed, we opt for a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The initial step involves a thorough medical history review, where your doctor will inquire about symptoms, onset, progression, and potential risk factors such as diabetes, alcohol use, nerve injury, or exposure to toxins.
During the physical examination, the doctor will assess sensory and motor function, looking for signs of nerve damage such as muscle weakness, loss of reflexes, or altered sensation. Tests like the monofilament test, which checks for loss of sensation in the feet, or nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG), which measure electrical activity in nerves and muscles, may be performed to evaluate nerve function.
Additional diagnostic tests can include blood tests to identify underlying conditions like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans to detect structural abnormalities pressing on nerves, and sometimes a nerve biopsy, where a small sample of nerve tissue is examined under a microscope to identify specific types of nerve damage.
Neuropathy Treatments in Tulsa, OK
The goal of treatment with neuropathy is to minimize any conditions that may be causing your symptoms, and to relieve painful symptoms as much as possible. Your doctor at Memorial Pain Management treats both the underlying condition and symptoms with a combination of therapies and appropriate medications that may include:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Pain killers
- Topical treatments and creams
- Physical therapy
- Platelet-rich plasma therapy
- Spinal cord stimulator
- Surgeries to relieve nerve pressure
Since our doctors specialize in interventional pain procedures, they may also recommend peripheral nerve blocks, injections, epidurals, and other cutting-edge treatments meant to reduce nerve pain. With these techniques, they can effectively reduce the severity of your pain and the amount of time you’re affected by painful symptoms. These treatments may also help you sleep better and increase your ability to move with more ease, ultimately improving the overall quality of your life.
To learn more about the treatments for neuropathy, call the Memorial Pain Management office location that’s most convenient for you or schedule a consultation online.
Peripheral Neuropathy Treatments
Treatment for peripheral neuropathy aims to manage symptoms and address the underlying cause. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment may include the following.
- Medications to reduce pain signals
- Nutritional supplements
- Physical therapy
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS)
- PRP therapy
Diabetic Neuropathy Treatment
Treatments for diabetic neuropathy focus on managing pain, controlling blood sugar levels, and addressing complications to improve the patient’s quality of life. Some key treatments include the following.
- Blood sugar control
- Pain relievers, anti-seizure medications, antidepressants, and topical treatments
- Lifestyle modifications and home remedies, such as foot care, a healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation
- Physical or occupational therapy
- Spinal cord stimulator
Treatment for Neuropathy in Legs and Feet
Treatments for neuropathy in the legs and feet focus on relieving pain, managing underlying causes, and improving quality of life. Key approaches include medications such as pain relievers, anti-seizure drugs like gabapentin and pregabalin, and antidepressants like amitriptyline or duloxetine. Topical treatments, such as capsaicin cream or lidocaine patches, can provide localized pain relief.
Controlling blood sugar levels is crucial for diabetic neuropathy. Physical therapy can enhance strength and balance, while proper foot care helps prevent complications. Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and smoking cessation, support overall nerve health. Alternative treatments like acupuncture and biofeedback may also offer symptom relief.
Neuropathy FAQs

Can Diabetic Neuropathy Be Reversed?
Diabetic neuropathy cannot typically be fully reversed, but its progression can be slowed, and symptoms can be managed effectively with proper treatment. Tight blood sugar control is crucial, as maintaining blood glucose levels within the target range can prevent further damage to sensory nerves and sometimes improve symptoms. Managing pain through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes like regular exercise and a healthy diet can also enhance quality of life.
How Long Can You Live With Neuropathy?
Neuropathy itself is not usually life-threatening, and many people can live for many years with the condition, particularly if it is well-managed. The life expectancy of someone with neuropathy largely depends on the underlying cause and how effectively it is controlled. For instance, managing diabetes effectively can significantly reduce the complications and relieve pain associated with diabetic neuropathy.
While neuropathy can cause significant discomfort and impact quality of life, proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments can help individuals manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life over the long term.
What Is the Most Effective Treatment for Neuropathy?
The most effective treatment for neuropathy depends on the underlying cause and the specific symptoms experienced by the patient. Generally, a combination of treatments yields the best results. For diabetic neuropathy, tight blood sugar control is essential to prevent further nerve damage.
Pain relief can be achieved through medications like anti-seizure drugs (gabapentin, pregabalin), antidepressants (amitriptyline, duloxetine), and topical treatments (capsaicin, lidocaine). Physical therapy, regular exercise, and a healthy diet can improve overall nerve health and functionality.
What Does Neuropathy Feel Like?
Neuropathy often feels like tingling, burning, or prickling sensations, especially in the hands and feet. It can also cause sharp, stabbing, or electric-like pain, as well as numbness or a reduced ability to feel pain or temperature changes. Some people experience muscle weakness, a sensation of wearing gloves or socks when not, and heightened sensitivity to touch after peripheral nerve damage.
Is Neuropathy a Disability?
Neuropathy can be considered a disability if it significantly impairs a person’s ability to perform daily activities or work. The extent of disability depends on the severity and progression of the symptoms, such as chronic pain, muscle weakness, or loss of sensation, which can affect mobility, dexterity, and overall quality of life. In severe cases, neuropathy may qualify for disability benefits.
Is Neuropathy Hereditary?
Neuropathy can have hereditary components, depending on the underlying cause. Some forms of neuropathy are genetically linked and can be inherited, such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and certain types of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies. These conditions are caused by genetic mutations that affect the structure and function of nerves. However, not all neuropathies are hereditary; many are acquired due to factors like diabetes, infections, or exposure to toxins.
What Kind of Doctor Treats Neuropathy?
Neuropathy is typically treated by several types of healthcare professionals depending on the underlying cause and specific symptoms. Neurologists are specialists who often diagnose and manage neuropathy, especially when it involves conditions affecting the nerves directly. Additionally, primary care physicians, endocrinologists (for diabetic neuropathy), rheumatologists (for autoimmune-related neuropathies), and pain management specialists may also be involved in treatment.
Contact Memorial Pain Clinic for Neuropathy Treatment in Tulsa, OK
At Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, OK, we are committed to guiding you towards relief from neuropathic pain and improving your overall well-being. Our experienced team understands the challenges neuropathy can bring and strives to offer tailored treatment plans that meet your unique needs.
Whether you’re seeking pain management strategies, rehabilitation services, or expert guidance on managing neuropathy symptoms, we are here to support you every step of the way. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a more comfortable and active lifestyle.
