Are you experiencing hand pain but not sure what’s causing it? Our hand pain diagram can help you identify the source of your discomfort based on where it hurts. At Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, Oklahoma, we’re dedicated to helping you find relief from chronic hand pain and wrist pain.
If your symptoms are affecting your daily life, we can create a treatment plan to help you manage hand pain and get back to doing what you love.
Call (918) 200-9944 or contact us online to speak with a healthcare provider today.
Hand Anatomy
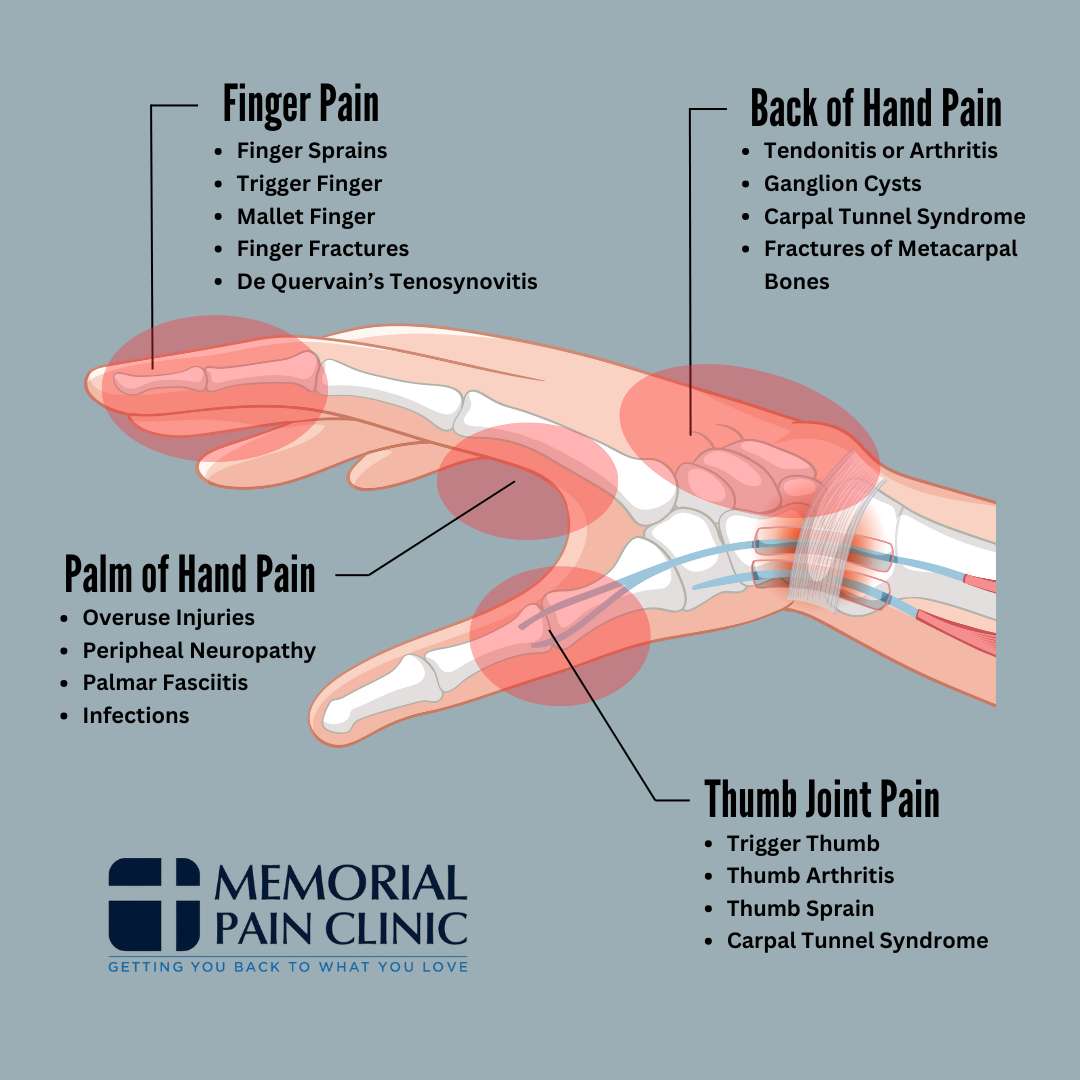
Understanding the anatomy of your hand can help you identify the source of your hand or wrist pain. Your hand is a complex structure composed of bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels, all working together to provide a wide range of movements and sensory and motor functions.
- Bones: Your hand contains 27 bones. These include the carpal bones (eight small bones that make up your wrist), the metacarpal bones (five bones that form the middle part of your hand), and the finger bones or phalanges (14 bones in your fingers and thumb). These bones connect to the radius bone and ulnar bone in your forearm at the wrist joint and distal radioulnar joint.
- Joints: The joints in your fingers and thumb, such as the proximal interphalangeal joint and middle or end joints, allow for bending and straightening. The thumb metacarpal joint gives your thumb a wide range of motion, making it easier to grip objects.
- Muscles: Your hand’s movement is controlled by both intrinsic muscles (located within the hand) and extrinsic muscles (located in the forearm). The thenar muscles control thumb movements, while the hypothenar muscles control the pinky finger. The interossei muscles help spread your fingers apart, and the lumbrical muscles assist in bending your fingers.
- Tendons and Ligaments: Flexor tendons and extensor tendons connect muscles to bones, allowing you to move your fingers and wrist. Collateral ligaments stabilize your finger joints, and the volar plate prevents your fingers from bending backward.
- Nerves: Nerves like the median nerve, ulnar nerve, and radial nerve provide sensation and control to your hand. Compression or damage to these nerves can lead to conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, causing symptoms such as a “fingers burning” feeling or trouble gripping objects.
- Blood Vessels: The ulnar artery and radial artery supply blood to your hand, ensuring that tissues receive the nutrients they need.
- Tendinous Structures: Structures like the tendon sheath protect your tendons. Both the sheath and the tendon can become inflamed and lead to tendon sheath swelling, causing pain and limiting movement.
If you’re experiencing symptoms like stiffness and swelling or difficulty moving certain parts of your hand, knowing the anatomy can be the first step toward finding pain relief. At Memorial Pain Clinic, we can help you live pain-free with specialized hand and wrist pain treatment.
Back of Hand Pain (Dorsal Side of Hand Pain)
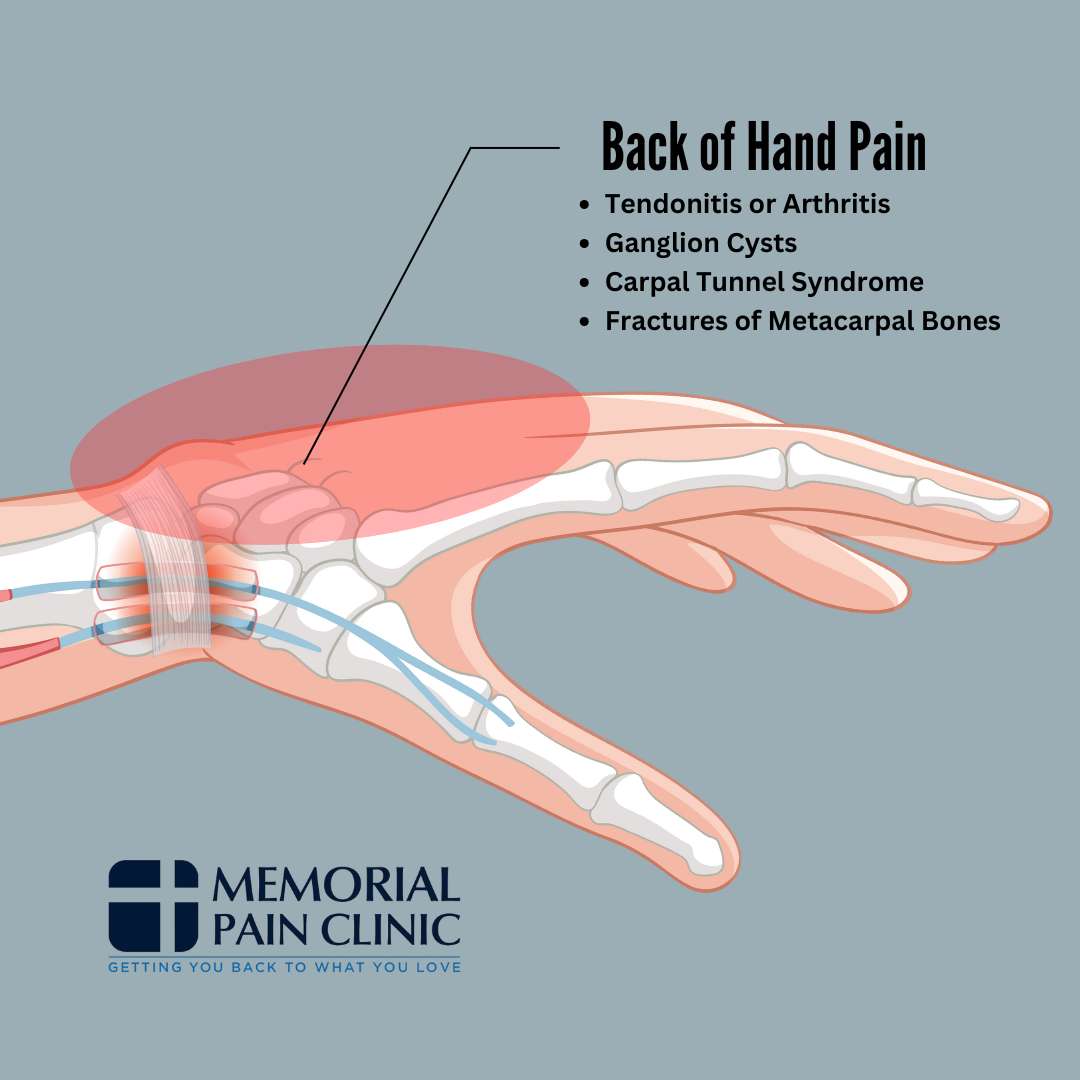
Pain on the back of your hand, also known as the dorsal side, can stem from various issues affecting the hand and wrist. Our hand pain diagram can help you get a better idea of what might be causing pain in this area.
Tendonitis or Arthritis
Inflammation of the flexor and extensor tendons can lead to tendon problems such as tendonitis, which results in pain when you move your hand or fingers. These tough cords connect muscles to the hand and wrist bones, and when they become irritated or inflamed, they can severely limit your hand’s ability to function properly. If left untreated, tendonitis can worsen over time, making even simple movements painful.
Other common tendon disorders like tennis elbow and baseball elbow can also contribute to hand pain. While these conditions mainly affect the elbow, they can cause pain that radiates down the arm into the hand and fingers. This can lead to tendon problems that result in pain when moving your hand or fingers. You might experience a “fingers swollen” feeling or difficulty performing everyday tasks due to the strain on the tendons connecting your muscles to your bones.
Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can also cause stiffness, swelling, and pain, further limiting movement and causing discomfort. If you’re facing these symptoms, arthritis treatment can improve your hand’s function and reduce pain.
Ganglion Cysts
A ganglion cyst is a soft tissue tumor that often appears as a lump on your hand or wrist. They are typically attached to a joint capsule or tendon sheath. You might notice an apparent cyst and localized swelling near the wrist joint or the base of your fingers.
Here are a few characteristics of ganglion cysts:
- Soft to the touch
- Cysts can vary in size and may change over time
- Typically causes swelling, mild aching, and discomfort
- Difficulty with wrist movement, like bending your wrist backward
- Can cause a sensation of fingers burning if the cyst presses on nearby nerves
While these fluid-filled cysts are usually harmless, they can interfere with daily activities and cause chronic hand pain. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider at Memorial Pain Clinic to discuss chronic pain management options.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that can cause hand and wrist pain, making everyday tasks difficult. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist formed by carpal bones and ligaments. This tunnel includes the median nerve and flexor tendons, which play a major role in the hand’s sensory and motor functions.
When the median nerve becomes compressed within the carpal tunnel, you may experience numbness, tingling, and a sensation of fingers burning. These common symptoms affect the index finger and middle finger, but especially the thumb. You might also have trouble gripping objects or notice weakness in your hand.
Conservative treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome usually provide some relief. Resting the affected hand, wearing splints to prevent wrist movement, and incorporating gentle hand and wrist exercises can help relieve compression on the median nerve. Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can also reduce inflammation and ease pain.
However, in more severe cases, these measures may not be enough to fully resolve the issue, and more in-depth carpal tunnel treatment may be necessary to provide long-term relief and restore hand function.
Fractures of Metacarpal Bones
If you’ve suffered a break in one or more of your metacarpal bones, the long bones connecting your wrist bones to your finger bones, you’re likely experiencing significant hand pain. These fractures commonly occur due to direct trauma, such as a fall or sports injuries. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and difficulty moving your fingers or gripping objects.
Fracturing a metacarpal bone can make it difficult to manage hand pain on your own, and improper healing may lead to long-term issues with hand function. At Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, we offer treatment solutions to help you properly recover from metacarpal fractures and alleviate your hand pain.
Palm of Hand Pain
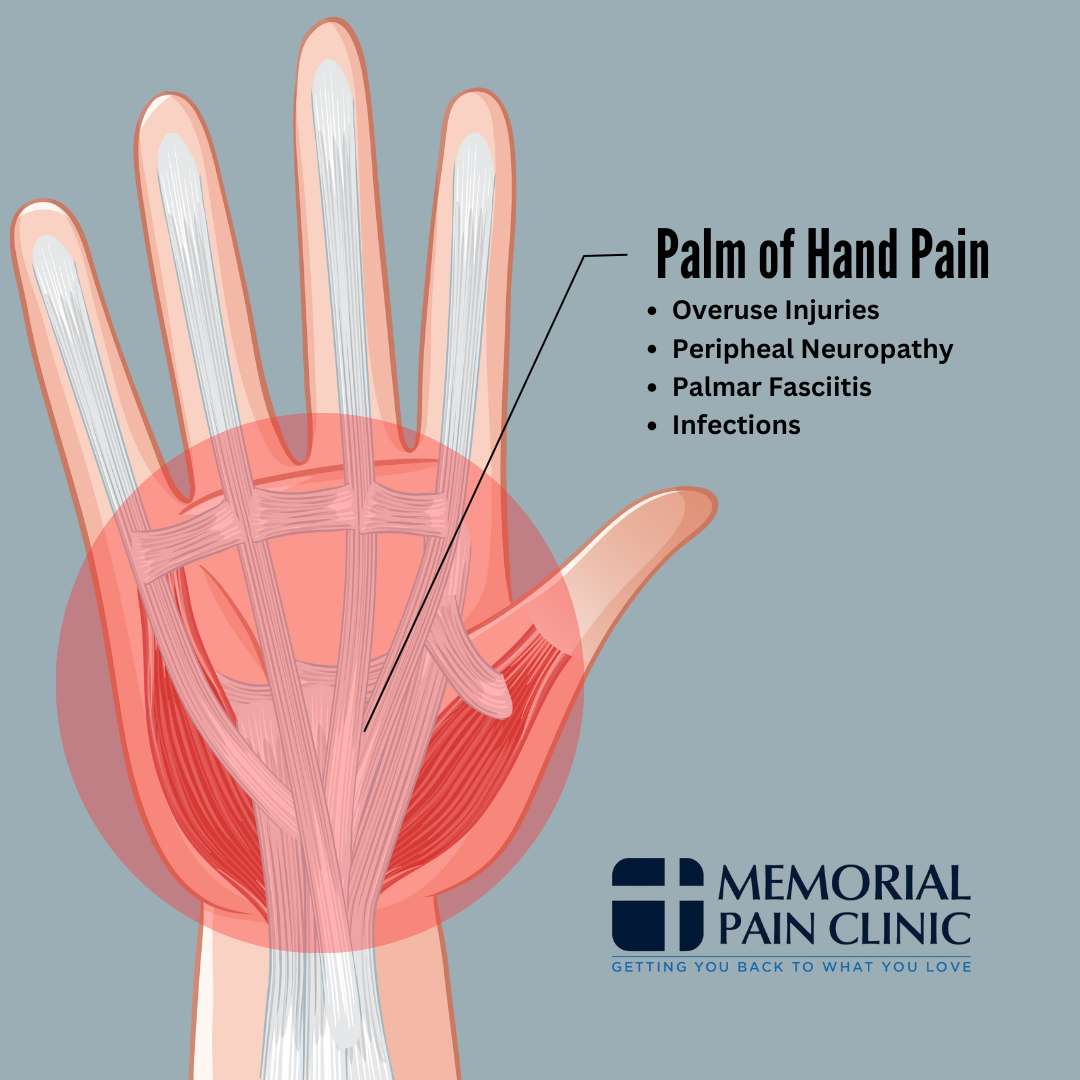
This hand pain diagram can help you pinpoint the exact source of pain in the palm of your hand, making it easier to understand what might be causing your discomfort. By identifying the location of your hand pain, you can narrow down potential causes like overuse injuries, peripheral neuropathy, or palmar fasciitis.
Understanding these pain patterns can guide you toward the appropriate treatment to relieve your symptoms and regain full function in your hand.
Overuse Injuries
Using your hands too much—like engaging in excessive exercise or doing the same motions repeatedly—can strain the fibrous tissues in your palm. This overuse affects the intrinsic muscles inside your hand and the extrinsic muscles in your forearm that control hand movements.
When these muscles and tissues become tired or irritated, you might feel pain or a constant ache in your palm. You may also find it hard to grip objects comfortably. Taking care of these overuse injuries early can help reduce your hand pain and stop it from getting worse.
Peripheral Neuropathy
If the ulnar nerve or radial artery is damaged, it can affect how your hand feels and moves. You might notice numbness, tingling, or weakness, especially on the side of your hand near your pinky and ring fingers, where the ulnar bone is located.
The ulnar nerve controls feeling and movement in that part of your hand, so if it’s injured or pinched, you might have trouble gripping things or lose sensation. Reduced blood flow from the radial artery can also cause similar issues, making it harder for your hand to work properly. Getting the right neuropathy treatment can help restore normal feeling and movement.
Palmar Fasciitis
Inflammation of the palmar fascia, the thick band of tissue running along the palm of your hand, can lead to pain and stiffness, a condition that is referred to as palmar fasciitis.
When the palmar fascia becomes inflamed, it tightens and restricts movement, making it difficult to fully open your hand or grasp objects. This inflammation can also cause swelling or a burning sensation, adding to the difficulty in performing everyday tasks. Treatment is important to relieve the inflammation and restore flexibility to your palm.
Infections
Infections in the hand and wrist can cause significant pain, often accompanied by localized swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area. These infections may result from small cuts, punctures, or even blisters that become infected. As the infection progresses, the pain can intensify, making it difficult to use your hand.
If left untreated, the infection can spread and lead to further complications, so it’s important to seek proper treatment to address the issue and relieve the pain in your palm.
Finger Pain
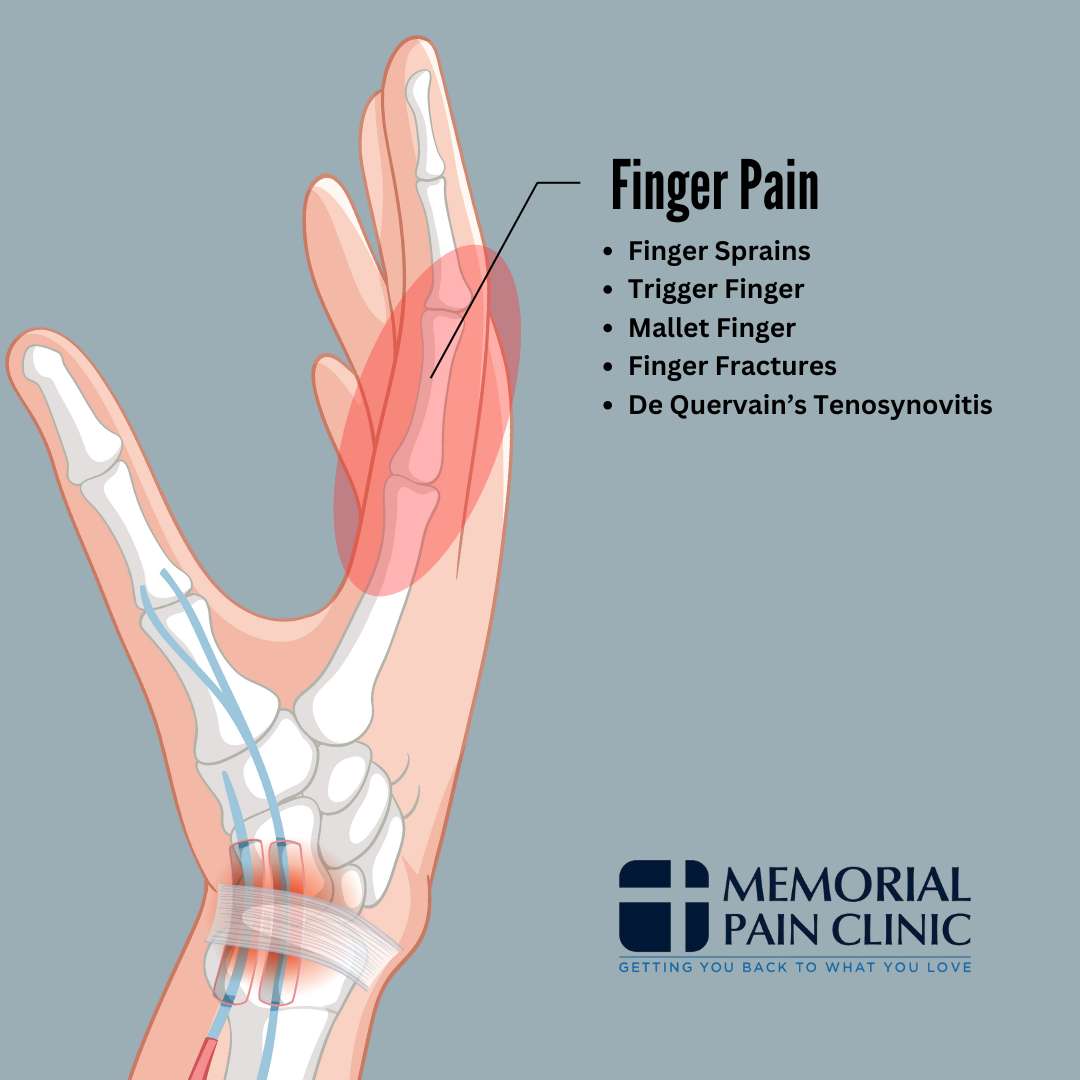
Our hand pain diagram can help you identify the exact location and potential cause of your finger pain, making it easier to understand what’s affecting your fingers. Whether you’re dealing with pain in your joints, tendons, or bones, this guide can point you toward common conditions like finger sprains, trigger finger, or finger fractures.
By pinpointing the source of your discomfort, you can take the next steps in finding the right treatment to alleviate your pain.
Finger Sprains
A sprain in your finger happens when the collateral ligaments, which are the bands of tissue that support and stabilize your finger joints, are stretched or torn. This usually occurs due to a sudden impact, such as jamming your finger during sports or a fall.
When these ligaments are damaged, it leads to pain and possibly swelling in the middle joint of the affected finger. You might also experience difficulty bending or straightening the finger fully, and the area can feel tender to the touch. In some cases, the finger may even appear bruised or feel weak.
Trigger Finger
Trigger finger is a condition where one of your fingers gets stuck in a bent position and may snap straight when you try to move it, like pulling a trigger. It happens when the tendon sheath in the finger becomes inflamed or irritated, causing the flexor tendons to catch as they move through the sheath. This leads to pain, stiffness, and a “clicking” feeling when bending or straightening the finger.
In more severe cases, the finger can become locked in a bent position, making it difficult to use. Steroid injections can help reduce inflammation and restore normal movement.
Mallet Finger
Mallet finger occurs when the extensor tendon at the tip of your finger is damaged, often from an injury like jamming your finger while playing sports. This injury makes it difficult or impossible to straighten the tip of the finger, leaving it bent down. You might also experience pain, swelling, and bruising around the middle or end joints of the finger. Surgery may sometimes be needed to repair the tendon and restore full function.
Finger Fractures
A finger fracture happens when one of the bones in your fingers breaks due to trauma, like a fall or impact. The three middle fingers, as well as the pinky and thumb, are all at risk for fractures, which can cause severe pain, swelling, and difficulty moving your hand and wrist. Proper treatment is essential to ensure the bone heals correctly, which could involve splinting, casting, or even surgery to realign the bone and restore full function to your hand and wrist.
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a painful condition that affects the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. The condition occurs when the tendons around the base of the thumb, particularly the abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis, become irritated or inflamed. This inflammation makes it difficult to move the thumb and wrist, especially when performing motions like grasping or pinching.
Common symptoms include pain and swelling near the base of the thumb, and sometimes a catching or popping sensation. Treatment typically involves resting the hand, wearing a splint, and using anti-inflammatory medications, but more severe cases may require cortisone injections or surgery to relieve pressure on the tendons.
Thumb Joint Pain
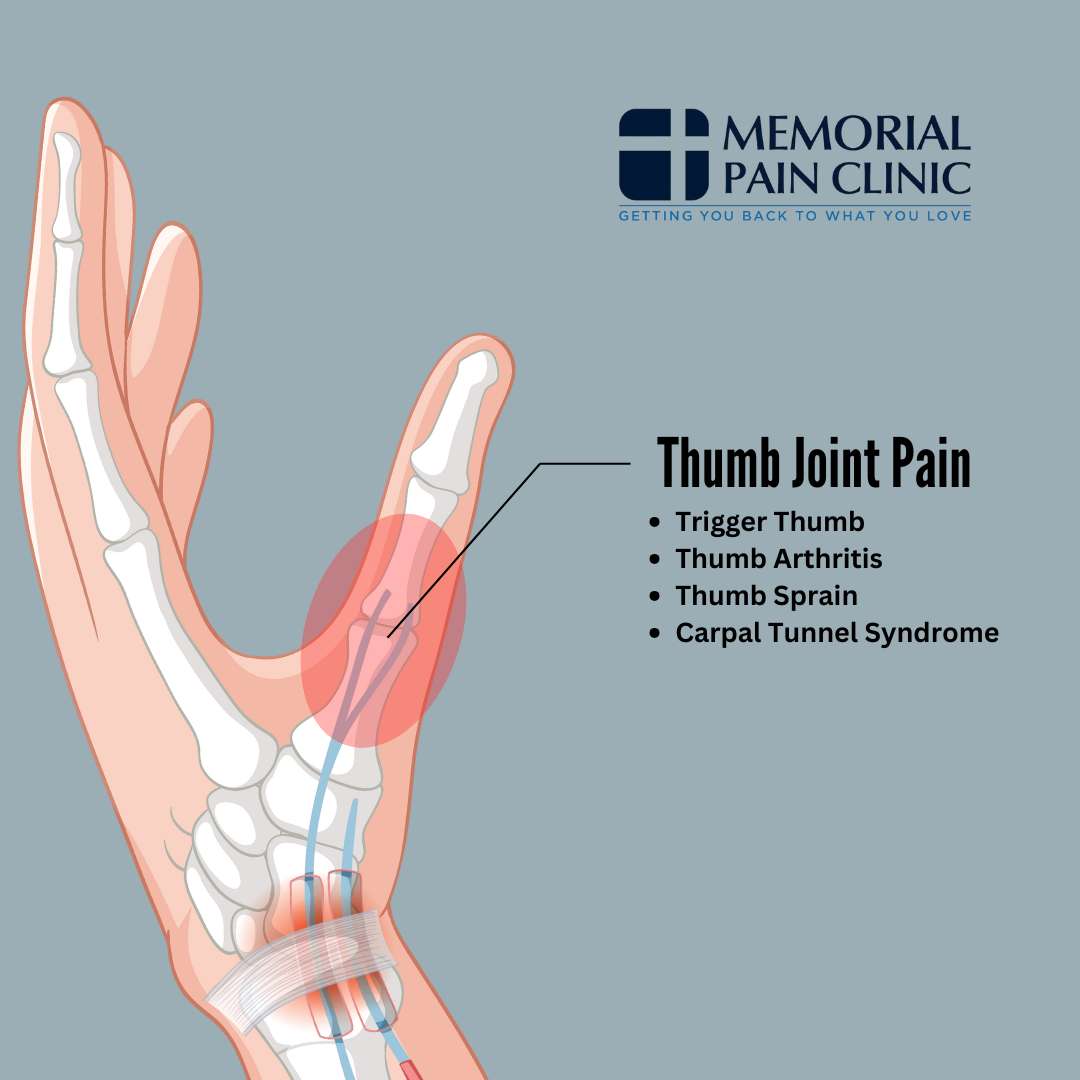
Thumb joint pain can affect your ability to perform everyday tasks, as the thumb plays a major role in hand function. Pain may stem from conditions like thumb arthritis, trigger thumb, or a thumb sprain, which can cause stiffness, swelling, and discomfort.
Our hand pain diagram can help you identify the exact source of your pain by showing you where these conditions typically occur in the thumb. By understanding where the pain originates, you can take the necessary steps to find the right treatment and relief for your thumb joint issues.
Trigger Thumb
Like trigger finger, trigger thumb happens when the area around the tendon in your thumb becomes swollen. This tendon sheath swelling makes it hard for the tendon to move smoothly when you try to bend or straighten your thumb. You might feel a popping or clicking when you move your thumb, especially when trying to grip things or make a fist.
In more severe cases, the thumb can get stuck in a bent position and won’t straighten easily. This can cause pain and stiffness, and treatment might include wearing a splint, taking anti-inflammatory medication, or getting a steroid injection to reduce the swelling and help your thumb move smoothly again.
Thumb Arthritis
Over time, the joint at the base of your thumb, called the thumb metacarpal joint, can wear down, leading to arthritis. This happens when the cartilage that cushions the bones breaks down, causing the bones to rub together.
As a result, you might feel pain, stiffness, and a swollen feeling at the base of your thumb, making it hard to grip or pinch things. The adductor pollicis muscle, which helps you bring your thumb toward your palm, can also be affected, making it even harder to move your thumb.
If left untreated, the pain can get worse, and treatment options might include wearing a splint, taking medication, or even surgery if needed.
Thumb Sprain
An injury to the volar plate or collateral ligaments in your thumb can cause pain and make it hard to move your thumb.
The volar plate helps keep the thumb joint stable and stops it from bending too far backward, while the collateral ligaments support the sides of the joint. If these areas get injured, you might feel pain, swelling, and have trouble gripping or pinching things. Your thumb may also feel weak, and simple tasks could become difficult. Getting the right treatment can help the thumb heal and return to normal.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
When the median nerve gets compressed in the carpal tunnel—a small passage in your wrist—it can cause numbness and weakness, especially in the thumb. This can make it hard to grip things or hold objects because the nerve controls feeling and movement in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. You might notice tingling or a weak grip, making everyday tasks difficult.
If the pressure on the nerve isn’t treated, these symptoms can worsen over time. Wearing a splint, doing physical therapy, or sometimes surgery can help relieve the pressure and improve how your hand works.
Hand Pain Relief Treatments in Tulsa, OK
If you’re experiencing hand pain in Tulsa, OK, there are various treatment options available to help you find relief.
Depending on the cause of your pain—whether it’s carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, or a tendon injury—conservative treatments like wearing splints, physical therapy, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. For more severe cases, possible cortisone injections or even surgery may be necessary to restore proper function and relieve discomfort.
At Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, we offer personalized care to help you manage and overcome hand pain so you can get back to doing what you love.
Contact a Hand and Wrist Pain Doctor in Tulsa at Memorial Pain Clinic
Don’t let hand pain hold you back from enjoying your life. At Memorial Pain Clinic in Tulsa, we specialize in providing effective, personalized treatments to help you find relief and regain full function in your hands. Whether you’re dealing with carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, or other hand and wrist conditions, our experienced team is here to support you every step of the way.
Call (918) 200-9944 or contact us online to schedule an appointment and start your journey toward pain relief today.

